Types of Volcanoes: Calderas
Pululahua caldera, Ecuador
Image Credit: MBG
Poas Volcanic Caldera, Costa Rica
Image Credit: MBG
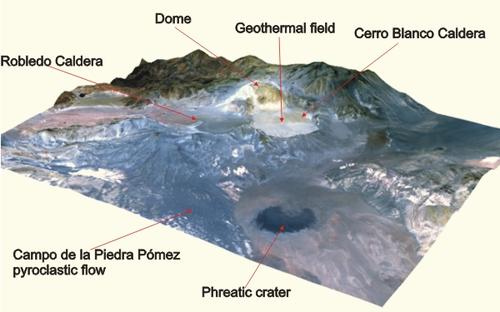
ASTER image combined with 3D elevation model of Cerro Blanco Caldera Complex, Argentina
Image Credit: MBG
Large morphological depressions, occasionally up to 50 km in diameter, are called calderas and are the result of the collapse ofthe volcanic edifice into their own underlying, partially emptied magma chamber. These large, often circular forms with nearly vertical walls are occasionally filled with water. After the formation of a caldera, the open space at the crater floor is subsequently filled in by more recent lava flows.
The reason for the shape of calderas is believed to be the collapse of the roof of a central reservoir of shallow magma. This may result when magma does not erupt from the central top but rather from the flanks of a volcano, leaving a gap between magma chamber and its respective roof. The structurally unstable roof collapses in a more or less regular form, reflected by the surface depression. The difference between craters and calderas is principally one of size and formation process: craters rarely exceed more than a few hundred meters in diameter. Caldera collapses are often associated with explosive volcanism. Funnel-shaped calderas are the result of flank collapses during non-regular roof collapses or erosive processes.